下面的写法:
<script type="text/javascript">
function ops(){
var win = window.open('','_blank');
win.onload = function(){
alert('ok');
};
win.location.href = 'test.html';
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="bb" onclick="ops();">
圆角三边 这里是内容
</div>
</body>
火狐里面是可以alert的,但是ie8就不行。
解决办法是子窗体调父窗体的方法模拟回调。(IE真是让人纠结。)
Continue reading window.open 子窗体的onload事件
[44/13]不要对员工太敏感,因为一个短期的考察结果错误的判断了长期的情况。
[]有些功力是无法用实际度量的,还是不要太急躁。--催化剂效应
西班牙人理论和英国人理论--看看英联邦国家和南美国家的现状就可以比较。
没有加班这回事--在中国企业,行得通吗?
人员流动的成本,有经验的和没经验的,对公司的感情?原始居民比率?
[62/31]
[70/39]越是成熟的公司,工作越无趣--你以为 google是例外?
第六章:苦杏仁苷
这与我的软件务实一个意思
[89/58]
一人一间办公室,做梦吧,中国
[102/71]
度量标准,度量往往是起反作用的。你怎么度量一个人?用评分制?中国高考是好参照。这是反话!
[113/82]
flow顺流,环境因子=不被打扰的时间/体力出勤时间.
电话
关门
一起工作的在一间办公室
[136/105]
窗子,空间,平等,特色……
爆米花不够专业
工作试讲,能力倾向性测试
[170/139]
公司 搬迁--说白了,还是要为员工考虑而不是其他的理由
员工的归属感,注重培养,培训,好的公司人员流动率低
[181/150]
当一个团队被完全确定了的程度时,他就完全丧失了自愈能力。
【被确定我觉得是指它的功效,能力等方面。大方法论-按照方法来,按部就班,那么最终会达到一个目的。做好了,是方法论定好了的,本该如此,没做好,那是你团队的问题。-这个论调你会经常碰到----这期间团队员工的付出努力一开始就被忽略了。
为什么会产生方法论?
你遇到一个比较复杂的问题时,你希望它的最终结果是顺利解决。那么你使用你“高瞻远瞩”的眼光和思考能力想出一个流程来解决这个问题,你认为你所想出的流程会解决大部分问题,这就是方法论。】
[183/152]
大方法论的疯狂
1:繁文缛节
2:极小量的方法
3:缺少责任感
4:缺少激励机制
[185/154]
脑力劳动员工强烈的独立意识,在新的前沿工作的牛仔意识。--我们应该尊重这种意识
完成方法汇集的方法
1:培训
2:工具支持
3:同级评审
不要轻易制定标准,规则
霍桑效应:人们在尝试新东西时,他们会表现得更好--应该是针对年轻人
标准必须要灵活宽松,让人有发挥的空间。所以不能太细。
[193/162]
胶东团队,只需要为他们排除障碍保证没人挡路,不需要传统的管理他们,他们自己会有动力。
一个团队的目的不是达到目的而是向目的看齐
[229/198]
公司亲和力建设策略
1:质量崇拜
2:提供更多令人满意的完型[closure]--制定合适时间段的目标,并让团队完成它。将大的目标分切为阶段式的目标。不要人觉得遥遥无期。
[233/202]
3:建立精英意识--要坐就要坐头等舱,施乐公司
4:允许和鼓励异端
5:保持和保护成功的团队
6:提供战略而不是战术指导
团队是平级的集合体,经理不是团队成员
经理的工作室把混乱拆散再分发出去
适当的的混乱是动力
一个项目中不要尝试太多的新技术,最好专注一方面的新技术,不要四面出击
社会学比技术或钱更重要
[264/233]
海报往往在贬低你
孩子之间不要竞争,团队成员之间也是如此
个人的成功注定要与整体的成功相联系
[273/242]
开始贬CMM,呵呵。
当今世界有关标准的成功都是有关标准接口的成功而不是产生这些接口的过程!
[282/251]
对于CMM,不要为了评级而评级。在提高纯熟度的时候,尽量不要考虑评分的事情。
[301/341]
人力成本,投资和支出是两回事。有经验员工的衔接时间。
公司的学习
如果流动量大,学习就不可能坚持
成功的学习的公司总是以强大的中层管理层为特点。
中层间需要保持畅通的交流,但是实际中往往存在相反的情况。
项目早期[设计阶段]可保持少量人员.
时间分割[一人同时多个任务]是浪费时间。
[322/291]
社区的重要性
[完]
------------------
如果是中国人写这样的言论,那似乎在说梦话。然而这本书都是通过实际的例子来说明的,可惜他们都不是在中国发生的。也就看看而已……
Continue reading 我看人件
一晃IT行业做得有些岁月了,虽然没参加过几次面试,但是几乎次次感受到“IT人相轻”,在工作中也是如此,对于同事,也倾向于证明别人是水枪。
也面试过别人一次,说实话那人确实很水,但我不想鄙视你呀,我想的是找一个工作的伙伴啊,所以我尽量平和的问一些你熟悉的问题呀,靠,你倒好,反倒比我还大大咧咧,倒鄙视起我来了,非得我旁边的外行问你才消得了你的气焰。
也常看javaeye的文章,经常是口水大战,火药味十足,我也只是笑笑,从来不发表言论,看看吵架也是猥琐的乐事。
有些人事业比较顺的时候,就发那么一篇闷骚的帖子,极力掩盖的炫耀一番,但是表面上看去确实彪悍了一番。哎,吵来吵去不都是些打工的人吗,多个一万两万的月薪,今天你鄙视我,明天我鄙视你,确实乐此不疲!
为什么与老板直接面试的时候感觉就好些呢,觉得他是求贤若渴一般。
为什么IT人士普遍有这种现象呢,得思考一番……
也许,是竞争的关系吧……
Continue reading IT人 相轻
Connection reset by peer: socket write error
除了其他原因[请求是页面关闭时发起的ajax请求],还有就是:
重复提交【用户点提交按钮很快的两遍,第二遍将第一遍冲掉】
Continue reading Connection reset by peer: socket write error
当拖拽一个树节点后将改动提交服务端后怎么样保证两处树结构一致,我的的做法是让树重新生成一遍。但是这里有个问题,extjs删除树时老是报错 removeChild this.ownerTree is null.这种情况发生在当拖拽一个树节点到一个未展开的树节点之下后删除此树时。我估计是由于刚才那个拖拽的节点造成的。
试过将整个treepanel重新构建,也是同样的错误。
原因是调用不可见节点的expand或select方法,因为这些节点的父节点没展开,这些节点不可见。
解决方法是将这些节点的父节点展开让这些节点可见。
Continue reading extjs tree 节点清空问题
对于软件人士来说,常常需要删除某个源码文件夹下面所有cvs,.svn文件夹。
现在介绍一个网上流传的注册表方法:
删除CVS代码:delCVS.reg
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Folder\shell\DeleteCVS]
@="Delete CVS Folders"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Folder\shell\DeleteCVS\command]
@="cmd.exe /c \"TITLE Removing CVS Folders in %1 && COLOR 9A && FOR /r \"%1\" %%f IN (CVS) DO RD /s /q \"%%f\" \""
将上面的代码保存为delCVS.reg 后双击此文件即可,可看到文件夹右键多出个Delete CVS Folders菜单.如图
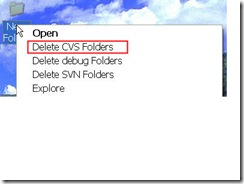
根据上面的代码,通过修改蓝色部分,你可以自己定制更多的右键菜单来删除不同的文件夹.
下面是删除svn文件夹的代码:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Folder\shell\DeleteSVN]
@="Delete SVN Folders"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Folder\shell\DeleteSVN\command]
@="cmd.exe /c \"TITLE Removing SVN Folders in %1 && COLOR 9A && FOR /r \"%1\" %%f IN (.svn) DO RD /s /q \"%%f\" \""
另外,常常遇到文件被锁,使用clean up也出错的情况,可以使用bat命令解决:
cd 到svn项目目录下,然后执行如下命令
del lock /q/s
就把锁删掉了。
Continue reading 添加删除.svn,cvs右键菜单的注册表 以及解锁问题
dom4j 的el.attributeValue是无法取到名空间类型的属性,简单点说就是带冒号的属性。
带冒号的属性是与名空间定义有关的,例如
<a xmlns="http://www.w3.org/xxx" xml:lang="en"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/xxx http://www.w3.org/xxx.xsd" >
这其中的蓝色部分就是特殊属性。
要取这样的属性在dom4j中应该这样做:
xmlns是名空间Element.getNamespaceURI()可以获得
xmlns:xsi --> Element.getNamespaceForPrefix("xsi").getURI()
xsi:schemaLocation --> el.selectSingleNode("@xsi:schemaLocation").getText()
Continue reading xml带冒号属性怎么获取
1 :gzip格式打包时被损坏:
今天花了一天时间,找出一个原来运行得好好的程序无法运行的原因:maven打包时将包资源里的gzip格式文件搞坏了。结果发布到产品环境下的gzip资源总是不可用,我勒个去!maven你怎么不去屎啊!
2:编译时图片(主要是png图片)资源拷贝损坏:
写swing程序时,放在源代码文件夹内的图片资源在生成到target/classes/文件夹下时出现损坏。
出现异常:
sun.awt.image.PNGImageDecoder$PNGException: crc corruption
原来是是将资源编译了
解决办法:
pom里面设置资源不编译:(但是maven默认就是false,不知怎么回事。)
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
<finalName>xxx</finalName>
</build>记住要清空再编译就发现图片好了。
Continue reading maven 导致文件损坏的问题
Computers are electronic devices that can follow instructions to accept input, process that
input, and produce information. There are four types of computers: microcomputers, minicomputers,
mainframe computers, and supercomputers.
Microcomputers, also known as personal computers, are small computers that can fit on a desktop.
Portable microcomputers can fit in a briefcase or even in the palm of your hand. Microcomputers are
used in homes, schools, and industry. Today nearly every field uses microcomputers.
One type of microcomputer that is rapidly growing in popularity is the portable computer,
which can be easily carried around. There are four categories of portable computers.
Laptops: laptops, which weigh between 10 and 16 pounds, may be AC-powered, battery-powered,
or both. The AC-powered laptop weighs 12 to 16 pounds. The battery-powered laptop weighs 10 to 15
pounds, batteries included, and can be carried on a shoulder strap.
Notebook PCs: notebook personal computers weigh between 5 and 10 pounds and can fit
into most briefcases. It is especially valuable in locations where electrical connections are not
available. Notebook computers are the most popular portable computers today.
Subnotebooks: subnotebooks are for frequent flyers and life-on-the-road types.[1] Subnotebooks
users give up a full-size display screen and keyboard in exchange for less weight. Weighting between
2 and 6 pounds, these computer fit easily into a briefcase.
Personal Digital Assistants: much smaller than even the subnotebooks. Personal Digital
Assistants (PDAs) weigh from 1 to 4 pounds. The typical PDA combines pen input, writing
recognition, personal organizational tools, and communication capabilities in a very small
package.
Minicomputers, also knows as midrange computers, are desk-sized machines. [2]They fall into
between microcomputers and mainframes in their processing speeds and data-storing capacities.
Medium-size companies or departments of large companies typically use them for specific purposes.
For example, they might use them to do research or to monitor a particular manufacturing process.
Smaller-size companies typically use microcomputers for their general data processing needs, such as
accounting.
Mainframe computers are larger computers occupying specially wired, air-conditioned rooms
and capable of great processing speeds and data storage. They are used by large organizations
business, banks, universities, government agencies—to handle millions of transactions. For
example, insurance companies use mainframes to process information about millions of policyholders.
Supercomputers are special, high-capacity computers used by very large organizations principally
for research purposes. Among their uses are oil exploration and worldwide weather forecasting.
In general, a computer's type is determined by the following seven factors:
The type of CPU. Microcomputers use microprocessors. The larger computers tend to use
CPUs made up of separate, high-speed, sophisticated components.
The amount of main memory the CPU can use. A computer equipped with a large
amount of main memory can support more sophisticated programs and can even hold several
different programs in memory at the same time.
The capacity of the storage devices. The larger computers systems tend to be equipped
with higher capacity storage devices.
The speed of the output devices. [3]The speed of microcomputer output devices tends to be
rated in terms of the number of characters per second (cps) that can be printed usually in tens
and hundreds of cps. Larger computers' output devices are faster and are usually rated at speeds
of hundreds or thousands of lines that can be printed per minute.
The processing speed in millions of instructions per second (mips). The term instruction
is used here to describe a basic task the software asks the computer to perform while also
identifying the data to be affected. The processing speed of the smaller computers ranges from 7
to 40 mips. The speed of large computers can be 30 to 150 mips or more, and supercomputers
can process more than 200 mips. In other words, a mainframe computer can process your data a
great deal faster than a microcomputer can.
The number of users that can access the computer at one time. Most small computers
can support only a single user, some can support as many as two or three at a time. Large
computers can support hundreds of users simultaneously.
The cost of the computer system. Business systems can cost as little as $500 (for a
microcomputer) or as much as $10 million (for a mainframe) and much more for supercomputer.
Continue reading it-e-01 four kinds of computers
As the amount of information on the Web grows, that information becomes ever harder to
keep track of and use. Search engines are a big help, but they can do only part of the work, and
they are hard-pressed to keep up with daily changes.
Consider that even when you use a search engine to locate data, you still have to do the
following tasks to capture the information you need: scan the content until you find the
information, mark the information (usually by highlighting with a mouse), switch to another
application ( such as a spreadsheet, database or word processor), paste the information into that
application.
A better solution, especially for companies that are aiming to exploit a broad swath of data
about markets or competitors, lies with Web harvesting tools.
Web harvesting software automatically extracts information from the Web and picks up
where search engines leave off, doing the work the search engine can't. Extraction tools automate
the reading, copying and pasting necessary to collect information for analysis, and they have
proved useful for pulling together information on competitors, prices and financial data or all
types.
There are three ways we can extract more useful information from the Web.
The first technique, Web content harvesting, is concerned directly with the specific content
of documents or their descriptions, such as HTML files, images or e-mail messages. Since most
text documents are relatively unstructured (at least as far as machine interpretation is concerned),
one common approach is to exploit what's already known about the general structure of
documents and map this to some data model.
The other approach to Web content harvesting involves trying to improve on the content
searches that tools like search engines perform. This type of content harvesting goes beyond
keyword extraction and the production of simple statistics relating to words and phrases in
documents.
Another technique, Web structure harvesting, takes advantage of the fact that Web pages
can reveal more information than just their obvious content. Links from other sources that point
to a particular Web page indicate the popularity of that page, while links within a Web page that
point to other resources may indicate the richness or variety of topics covered in that page. This
is like analyzing bibliographical citations— paper that's often cited in bibliographies and other
paper is usually considered to be important.
The third technique, Web usage harvesting, uses data recorded by Web servers about user
interactions to help understand user behavior and evaluate the effectiveness of the Web structure.
General access—pattern tracking analyzes Web logs to understand access patterns and
trends in order to identify structural issues and resource groupings.
Customized usage tracking analyzes individual trends so that Web sites can be personalized
to specific users. Over time, based on access patterns, a site can be dynamically customized for a
user in terms of the information displayed , the depth of the site structure and the format of the
resource presented.
Continue reading it-e-02 web harvesting
Pagination

